Principle of laser cutting
The laser is the abbreviation of the English words Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. The laser uses a property of the atom which is population inversion. The principle is to deflect an electron from its orbit to a higher orbit. The electron tends to naturally return to its original level, it restores the energy absorbed in the form of light radiation called photon. The laser uses a property of the atom which is the population inversion. This property was discovered in 1917 by the physicist Albert Einstein. It then remains Theoretical. It will take 50 years to find an application for this theory. It was in 1960 that Theodore Maiman physicist gets the first laser with a ruby. In 1967, Peter Holcroft cutting a stainless steel plate of 2.5 mm thick at a speed of 1 m / min under oxygen with a CO2 laser of 300 W and designs the first cutting head.
CO2 Lasers
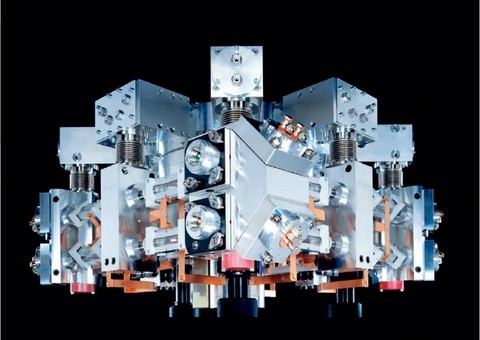
The CO2 laser is a gas mixture of CO2, nitrogen and helium ionized by an electric current to the excitement of it. CO² is the gas that creates the phenomenon. Nitrogen is the gas for this reaction. Helium is used to cool the mixture to him. The power of a CO² laser is proportional to the ionization length and speed of movement of GAS. Rated shape Square which developed the Laser measuring 8m long. 1 m² on two levels. The turbine located on the lower portion at the center circulates the gaseous mixture at high speed. On the front portion two cylindrical mirror is observed, out of the mirror and the bottom mirror. The left mirror passes only 50% of the power laser to maintain the phenomenon inside the cavity. Between the mirror blocks the discharge tubes shown here surrounded by the electrodes which sends an electric current through the tube to ionize the gas. Electric current can be continuously guy. He then gives a more stable beam quality. Laser radio frequency allows for better modulation of power. Its frequency is 13, 56 Mhz.
YAG LASER
The YAG laser or Garnet and Yttrium Aluminum is obtained from the excitation of a synthesis crystal by an electric current or a light source. The advantage of the YAG laser is that it is conductive optical fiber. It is ideal for robotic welding applications. The fiber laser has now compete Co² as it is now reaching powers of 6to 7 K Watt.
it is more versatile, it offers the possibility to cut materials such as copper or brass which is risky for the source of a laser Co². It is also more efficient in cutting high pressure nitrogen. The maintenance costs are much lower, the volume of cooling water is lower, there is no optical path, so more return mirror or cavity to change. The consumption of nitrogen is reduced as there is no pressurisation of the optical path. There are more turbine to the gas flow. The laser fiber is about 60% market share today. The laser fiber is cheaper to manufacture and operate. However it is still limited in strong steel thicknesses. Paradoxically it is slightly more expensive to buy so called for the costs of research and development, but above all not to compete Co² LASER market much more sharp to manufacture and which required very large investments by manufacturers .
laser fibre nouvelle génération
LASER DISQUE
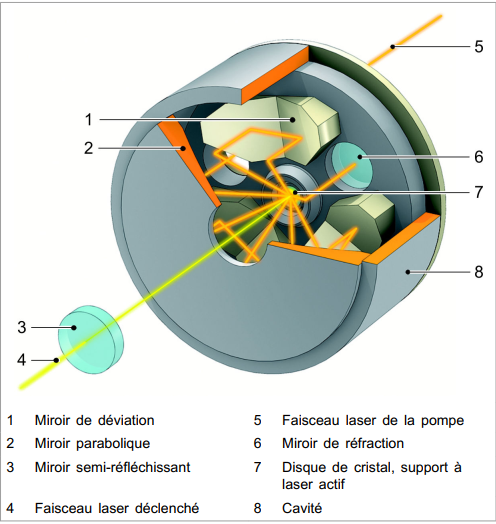
The active laser carrier is a thin Yb:YAG (ytterbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet) crystal disc. The disc laser is pumped using laser diodes. The laser beam is generated in the crystal disc and exits the cavity through a bore in the center of the parabolic mirror.
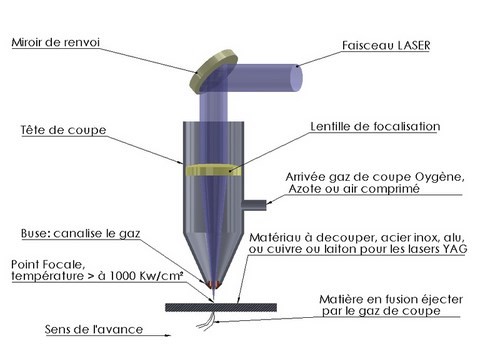
Principle of laser cutting
The principle is to focus a lot of energy on a very small area. This is done by a lens. Simply propel an assistance gas to chase away the material, cutting gas. The latter can be of three different types. Oxygen is used to cut steel, there for property to enable combustion. We are talking about black Cup. Nitrogen gives best results in stainless steel and aluminium. It is white cut, i.e. without carbon cutting. The steel can also be machined white Cup for parts to be painted and cannot be sanded.
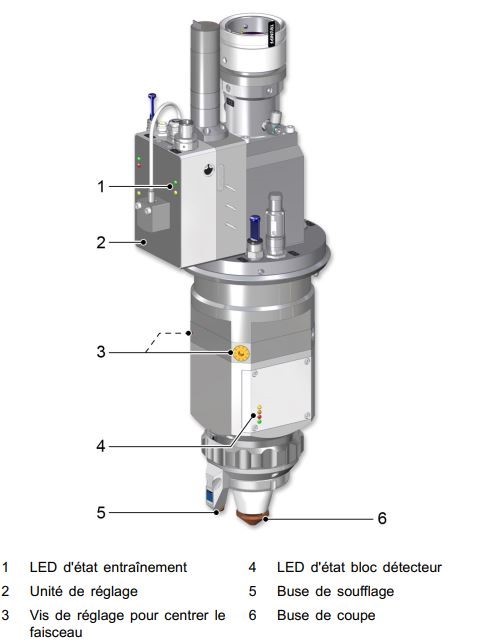
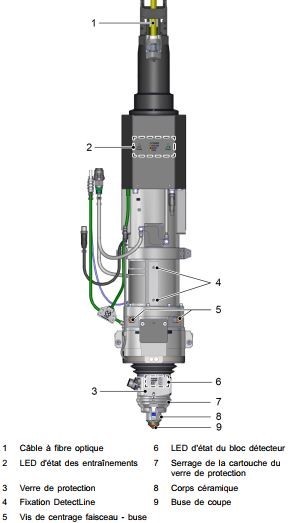
TETE DECOUPE LASER FIBRE
même principe que le LASER Co². Le faisceau laser est guidé de la source laser jusqu'à l'unité de coupe via le câble à fibre optique (LLK) et est focalisé par un jeu de miroir. Le gaz de coupe pousse la matière et aide à la combustion dans le cas de l'oxygéne et de l'aire comprimé.